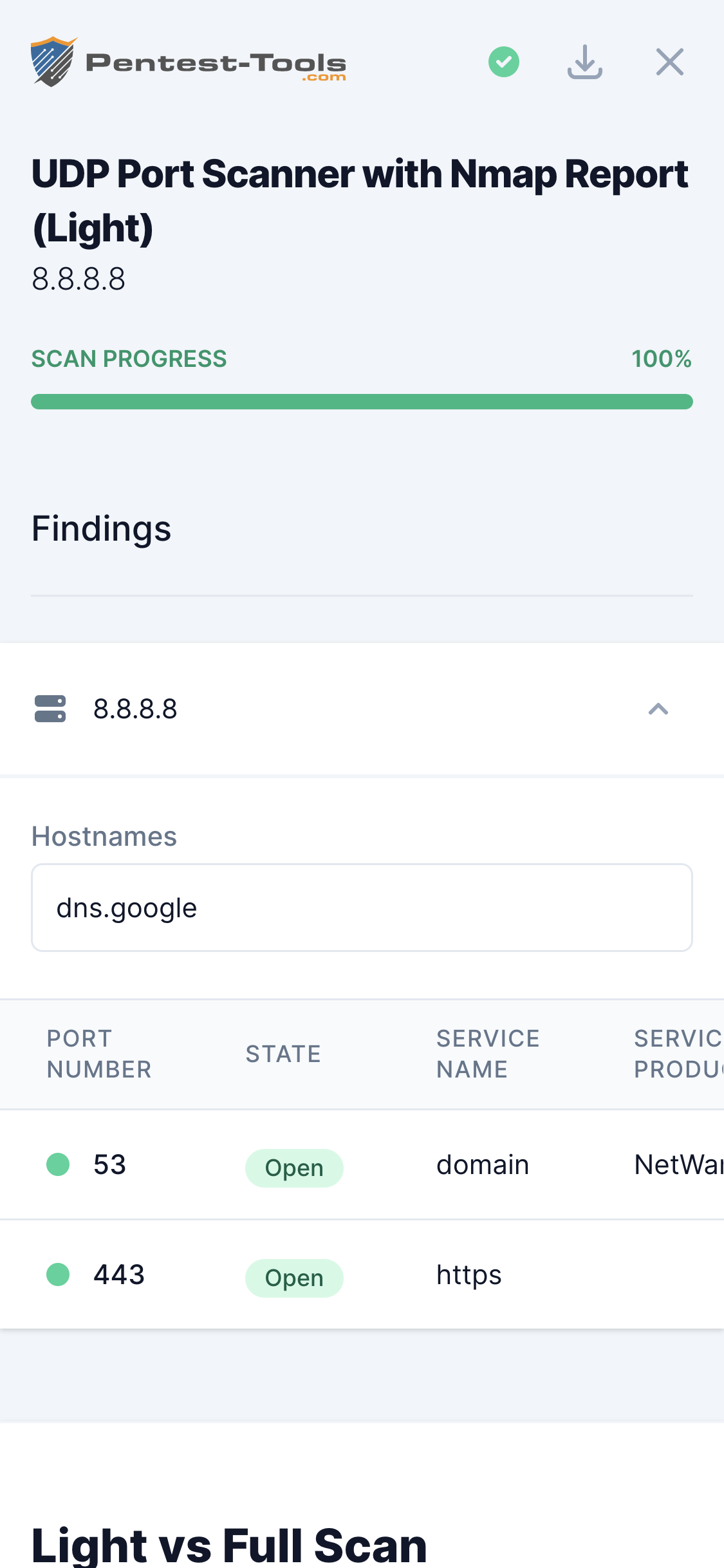
UDP Port Scan
Technical details
UDP is a transport layer protocol (the same as TCP) mainly used in network services such as DNS, NTP, DHCP, RTSP, TFTP, and others.
Even though UDP services are less popular than TCP services, having a vulnerable UDP service exposes the target system to the same risk as having a vulnerable TCP service. Hence, discovering all open UDP ports is important in a penetration test for achieving complete coverage of the security evaluation.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Target | This is the target to scan for open UDP ports. Can be specified as hostname or IP address |
| Ports to scan - Common | This option tells Nmap to scan only the top 10, 100, 1000, or 5000 most common UDP ports (Nmap --top-ports). Top 100 is the default scan option. |
| Ports to scan - Range | You can specify a range of ports to be scanned. Valid ports are between 1 and 65535. Because of the way UDP protocol works, scanning is pretty slow so if you specify a large range of ports, the scan can take up to several hours. |
| Ports to scan - List | You can specify a comma-separated list of ports to be scanned |
| Detect service version | In this case, Nmap will try to detect the version of the service that is running on each open port. In the case of UDP, this is possible only by sending UDP requests that can be understood by the tested service, otherwise, the service will not answer at all |
| Detect operating system | If enabled, Nmap will try to determine the type and version of the operating system that runs on the target host. The result is not always 100% accurate, depending on the way the target responds to probe requests |
| Don't ping host | If enabled, Nmap will no longer do host discovery before scanning (which is the default behavior). This option is useful when the target host does not respond to ICMP requests but it is up and it has open ports |
How it works
The tool is a web interface for Nmap, which is called with the proper parameters to provide speed and accuracy.
Behind the scenes, Nmap sends UDP packets to each port specified in the parameters. If the target responds with 'ICMP port unreachable', Nmap can be sure that the port is closed. Otherwise (no response received), the scanner cannot know if the port is open, firewalled or if the packet was lost on the way. In this case, Nmap will show you the status open|filtered for that port.
To make sure that a certain port marked as open|filtered is really open, you should enable the detection of the service version. Since this operation is really slow, you should do it in a second scan, only for the ports that were reported as open|filtered in the initial simple scan.